Generative AI with JAX
Wassim Kabalan
2025-10-01


Outline for This Presentation
- Introduction to Generative AI
Understand the mathematical meaning of generating data
- Deep dive into Generative Models
Explore the different framework and state of the art ways of generative AI
- JAX eco system
Learn core JAX transforms (jit, vmap, grad) and Flax tooling
- Hands on tutorial
Explore how generative AI can be used for cosmological inference
What is Generative AI?
What does “generate” mean?

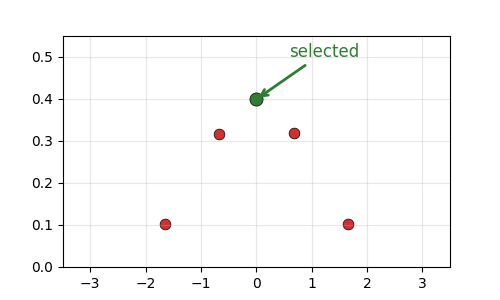
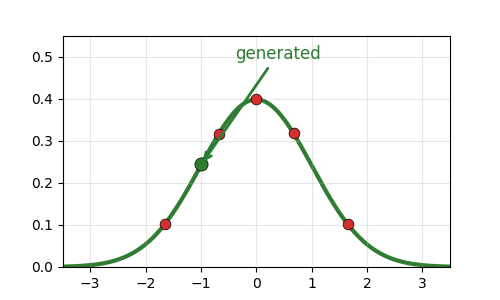
Key Idea: Generative AI
- Generative AI is about learning the underlying distribution \(p(\text{data})\) and sampling from it to generate images.
- The output of a generative model is a new data point.
- Generative is intrinsically related to probability distributions.
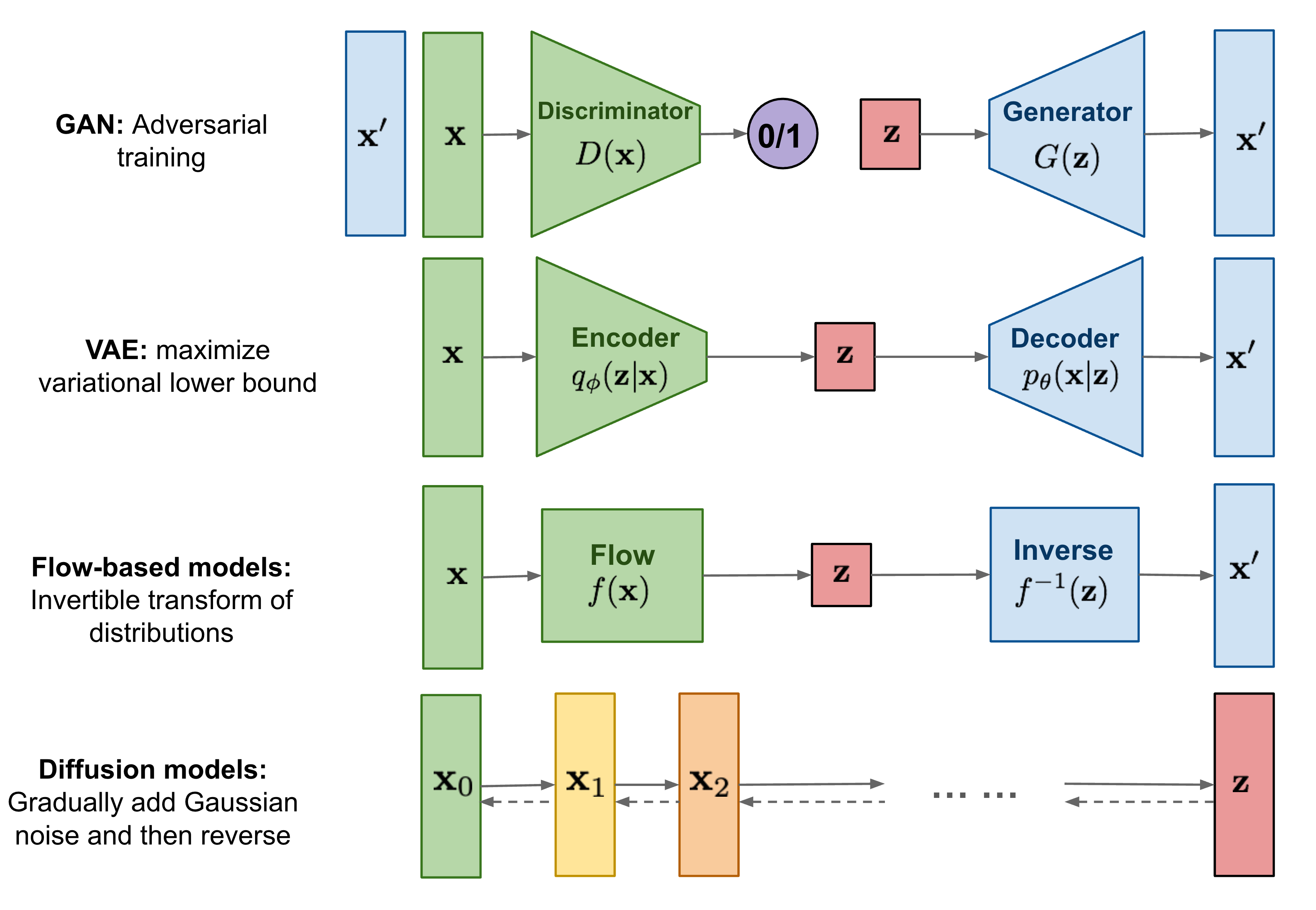
Generative Models
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
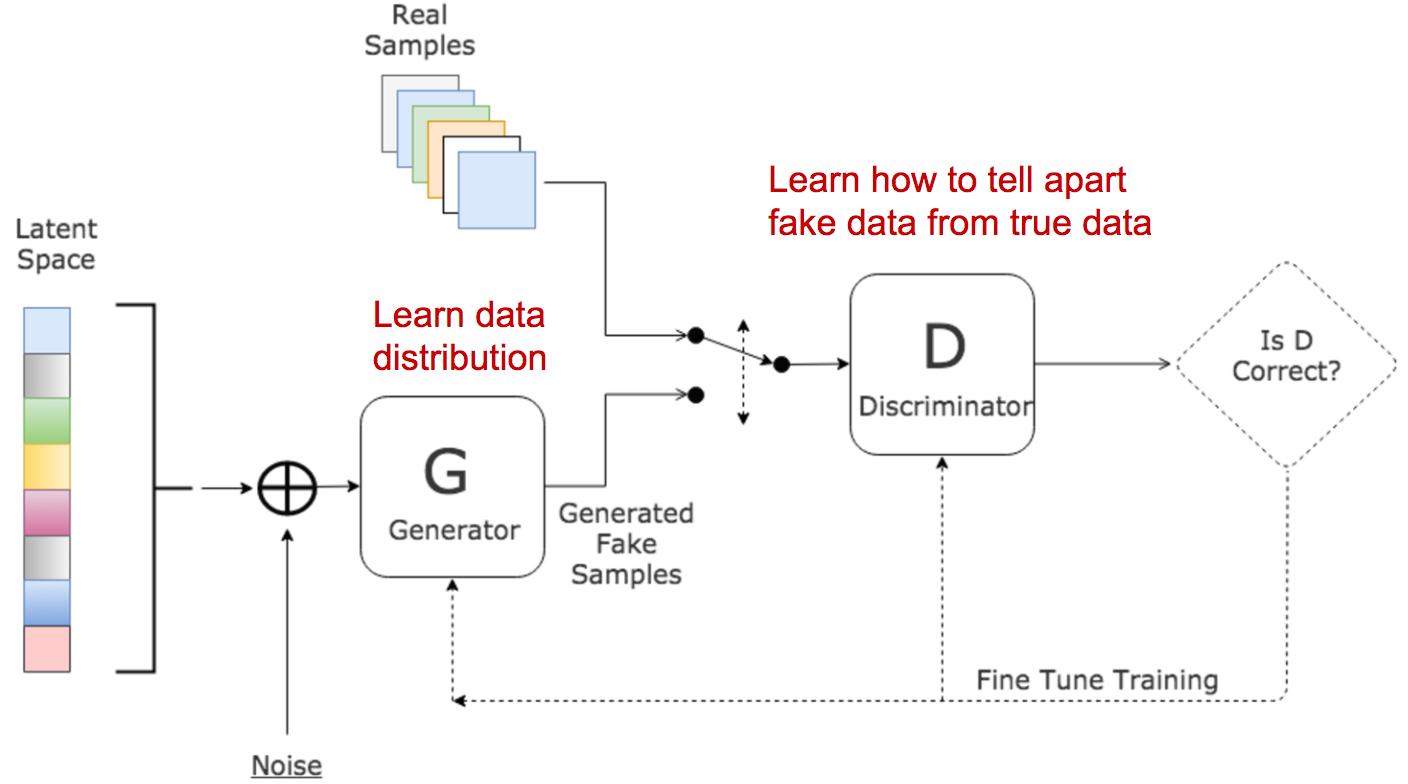

\[\min_G \max_D \mathbb{E}_{x\sim p_\text{data}}[\log D(x)] + \mathbb{E}_{z\sim p(z)}[\log(1 - D(G(z)))]\]
- Loss function
- Generator: produces samples G(z) to fool D
- Discriminator: estimates real vs fake probability D(·)
Advantages and Limitations
- Advantages: sharp samples; flexible implicit modeling; no explicit likelihood.
- Limitations: unstable training; mode collapse; sensitive to architecture and tricks.
Limitations with GANs
Unstable learning
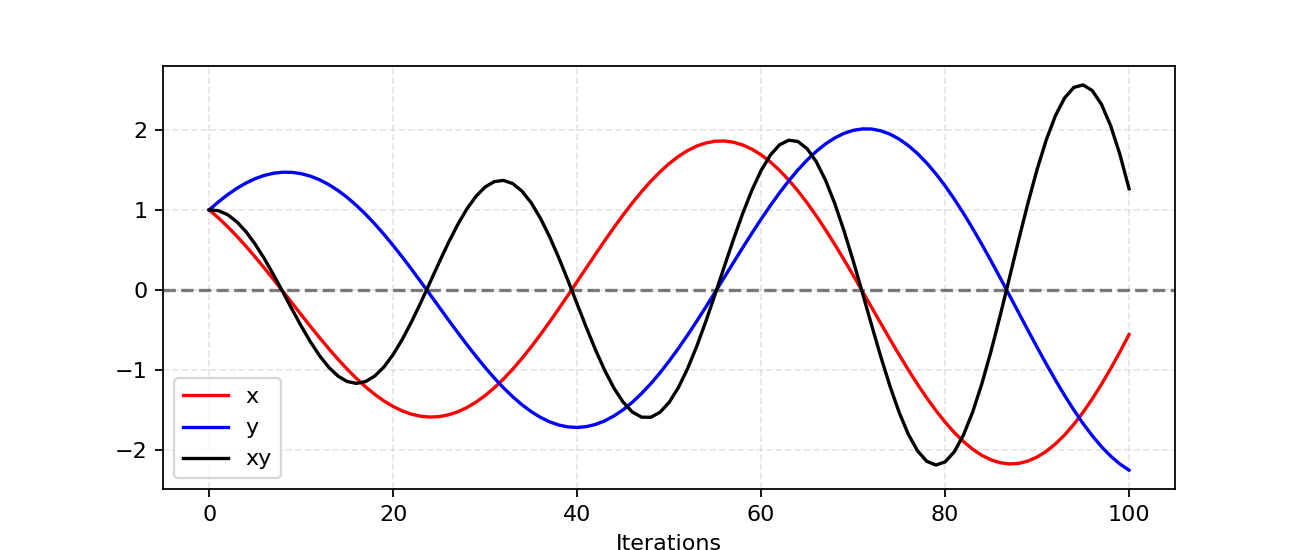
Mode collapse

Vanishing gradients
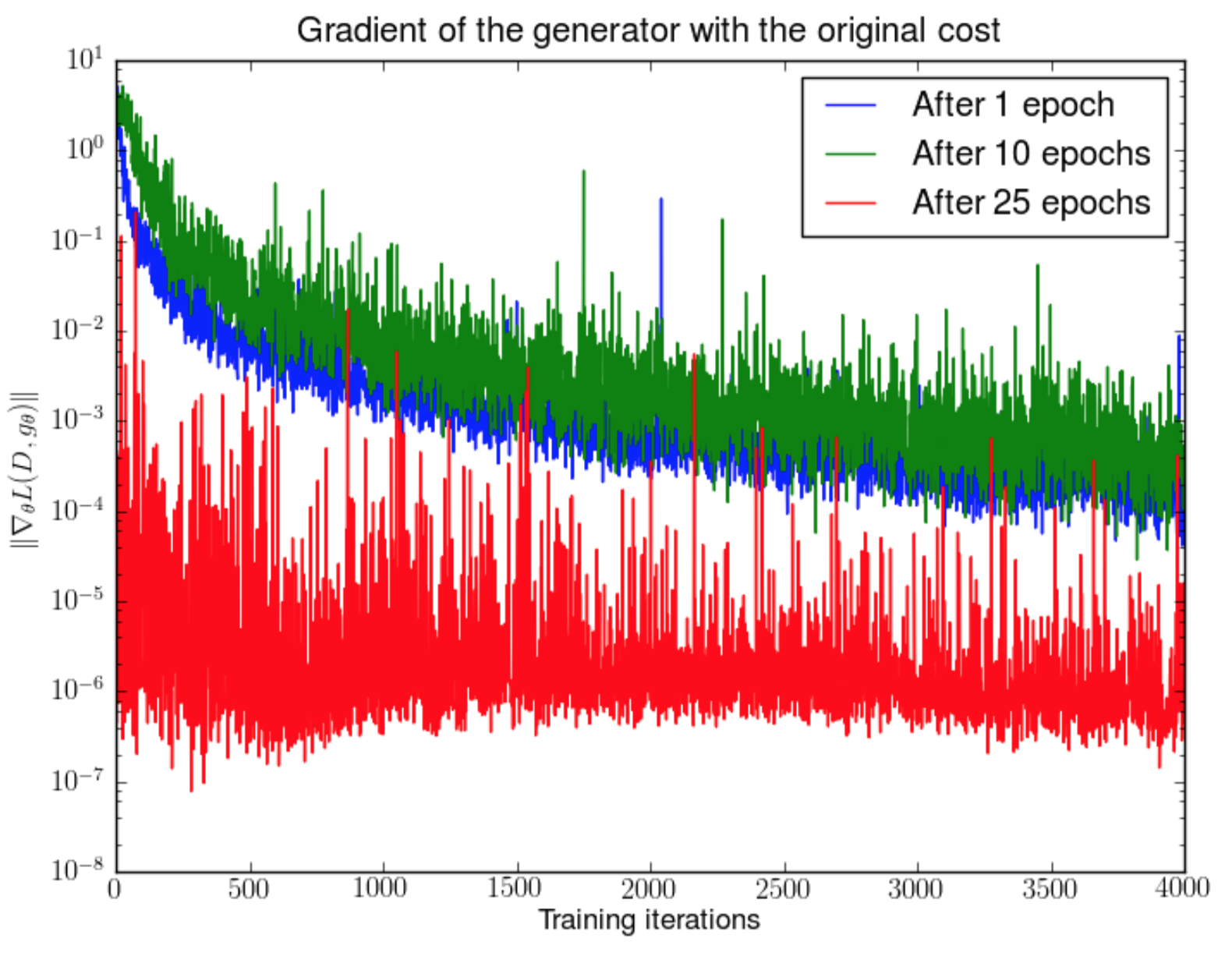
Some possible solutions
- Use WGAN for more stable training and stronger gradients.
- Add gradient penalty (WGAN-GP) to keep the critic smooth.
Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)
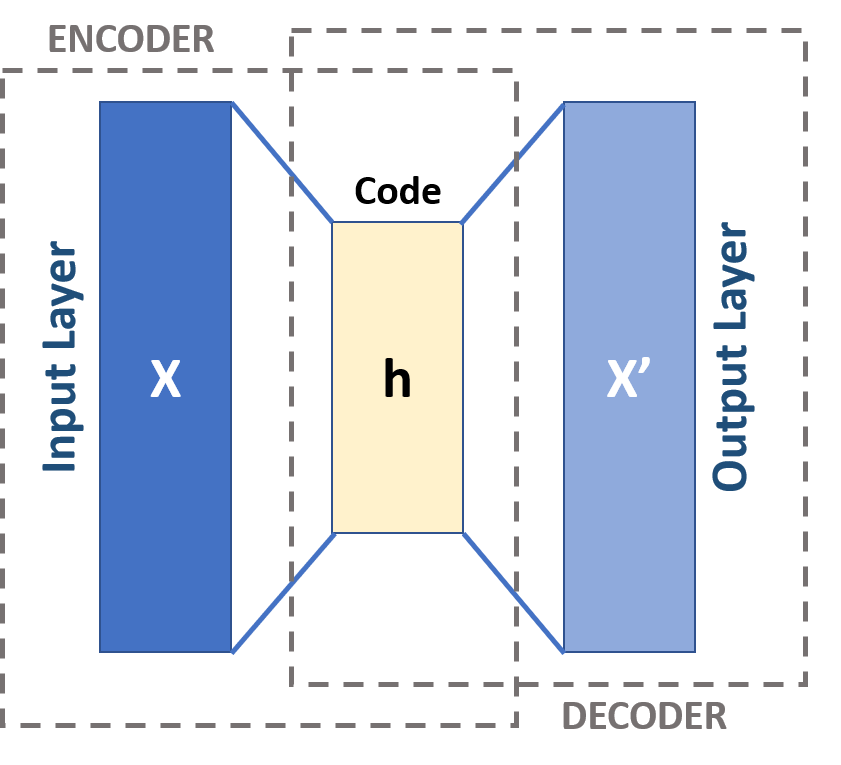
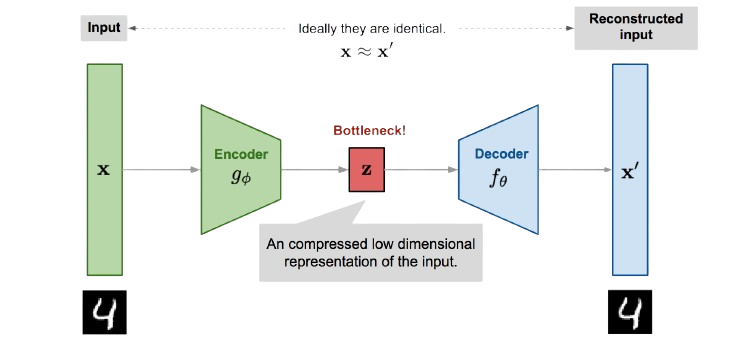
VAE takeaways
- VAE learn optimal compression into the latent space
- Represents a dataset by an easy to sample gaussian distribution
- Compared to GAN gives a better access to probability distribution
- Produces blurrier images than GANs

Evidence Lower Bound (ELBO):
\[\mathcal{L} = \mathbb{E}_{q_\phi(z|x)}[\log p_\theta(x|z)] - \text{KL}(q_\phi(z|x)\|p(z))\]
- Reconstruction: decoder quality
- KL Divergence: latent regularization
Reparameterization trick: \[z = \mu + \sigma \odot \epsilon, \quad \epsilon \sim \mathcal{N}(0,I)\]
VAE — Why KL matters (β-VAE)
Without KL regularization:
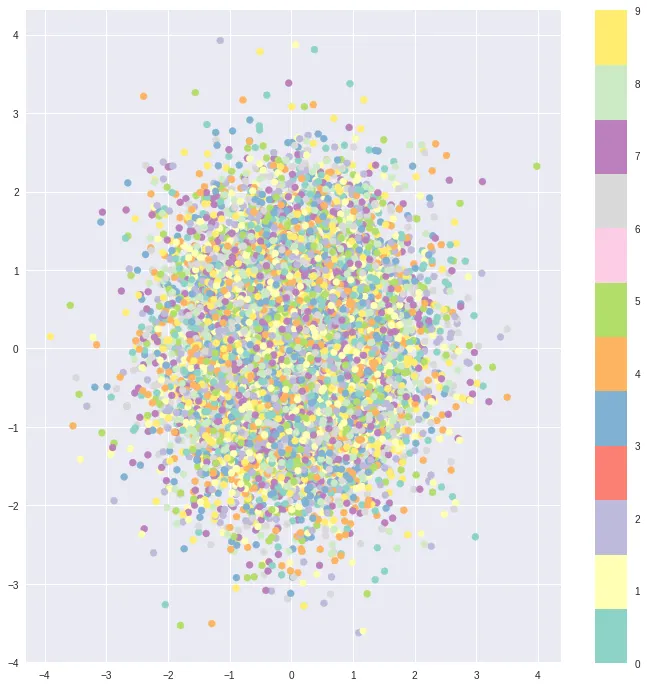
Latent space is unstructured
With KL regularization:
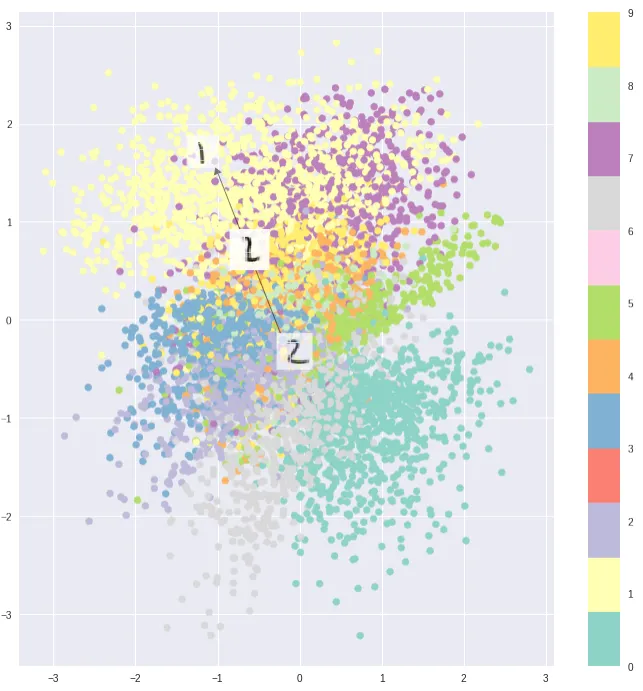
Organized, continuous latent space
β-VAE objective:
\[\mathcal{L}_\beta = \mathbb{E}[\log p_\theta(x|z)] - \beta \cdot \text{KL}(q_\phi(z|x)\|p(z))\]
- \(\beta > 1\): More disentanglement, less reconstruction
- \(\beta < 1\): Better reconstruction, less structure
- Limitation: Gaussian prior can bias toward simpler shapes
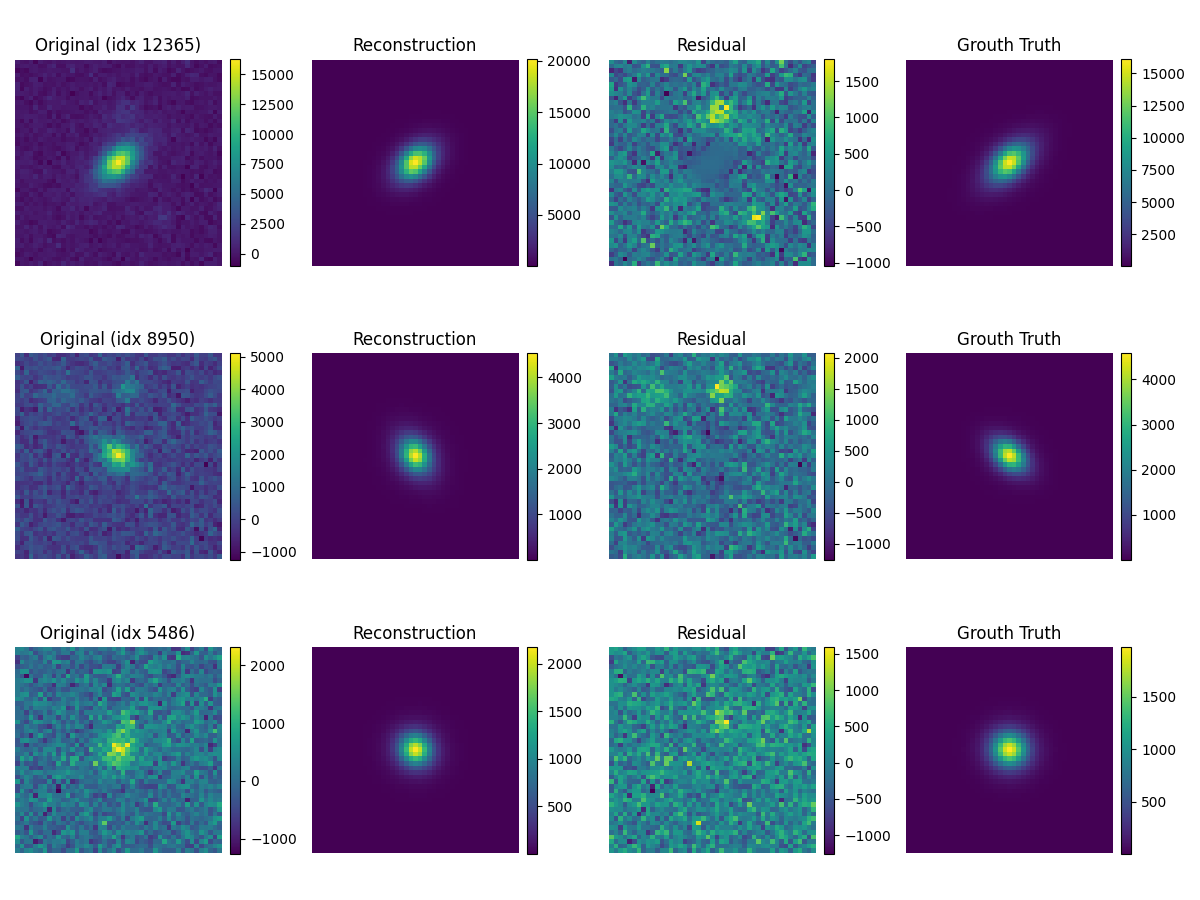
VAE in Cosmology (Deblending)

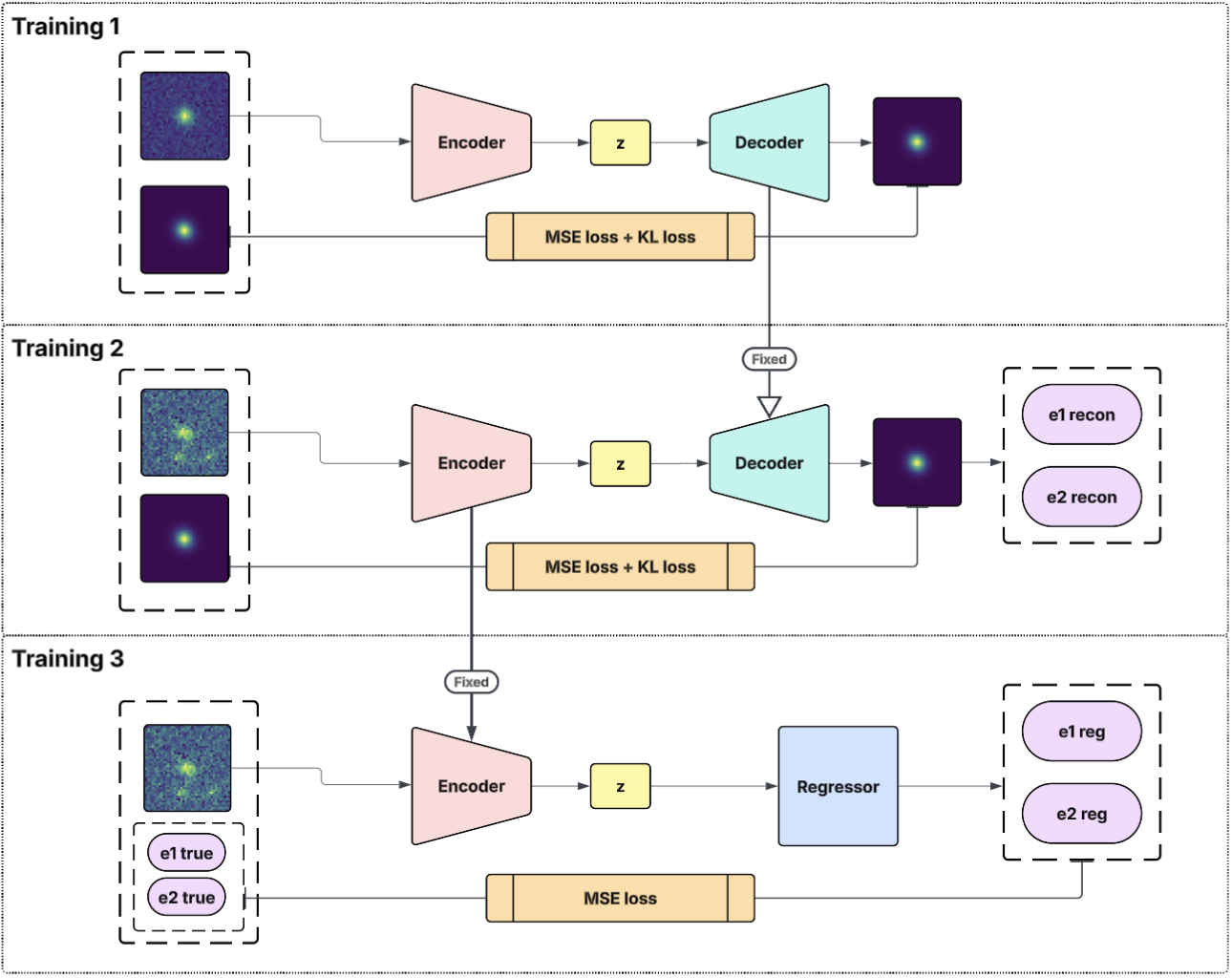
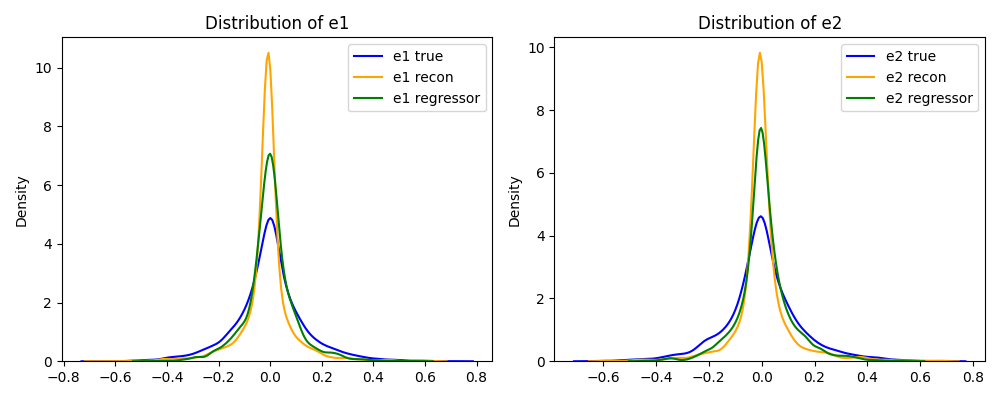
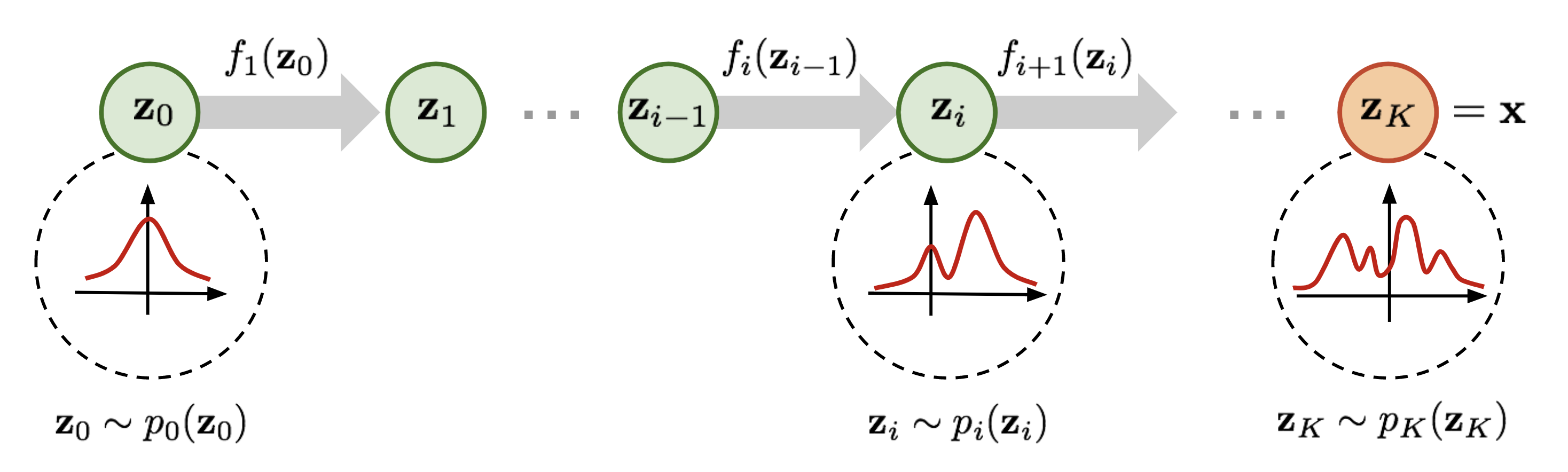
Normalizing Flows (Flow-based Generative Models)
Mappings: \(f(x) \to y\), \(g(y) = z\); \(z = g_{\theta}(x) = g_K \circ \cdots \circ g_1(x)\)
Log-likelihood
\[\log p_{\theta}(x) = \log p_Z\big(g_{\theta}(x)\big) + \sum_{k=1}^{K} \log \left|\det J_{g_k}\right|\]

Rezende & Mohamed (2015)
In short
- Gaussianize data: \(z = g_{\theta}(x) \approx \mathcal{N}(0, I)\).
- Exact likelihood: \(\log p_{\theta}(x) = \log p_Z(z) + \sum_k \log|\det J_{g_k}|\).
- Generate via inverse: \(x = f_{\theta}(z)\), \(z \sim p_Z\).
Coupling Layers : Forward vs Inverse
Coupling layer computation graph
Forward (x → y)
- Split \(x=(x_a, x_b)\) by mask.
- Conditioning network on kept half: \((s, t) = \text{NN}(x_a)\).
- Affine update (element-wise):
\[ y_a = x_a, \qquad y_b = x_b \odot e^{s(x_a)} + t(x_a). \]
Inverse (y → x)
Given \((y_a, y_b)\):
- Recompute \((s, t) = \text{NN}(y_a)\).
- Invert the affine on the transformed half:
\[ x_a = y_a, \qquad x_b = \big(y_b - t(y_a)\big) \odot e^{-s(y_a)}. \]
Masked Autoregressive Flow (MAF) vs Inverse Autoregressive Flow (IAF)
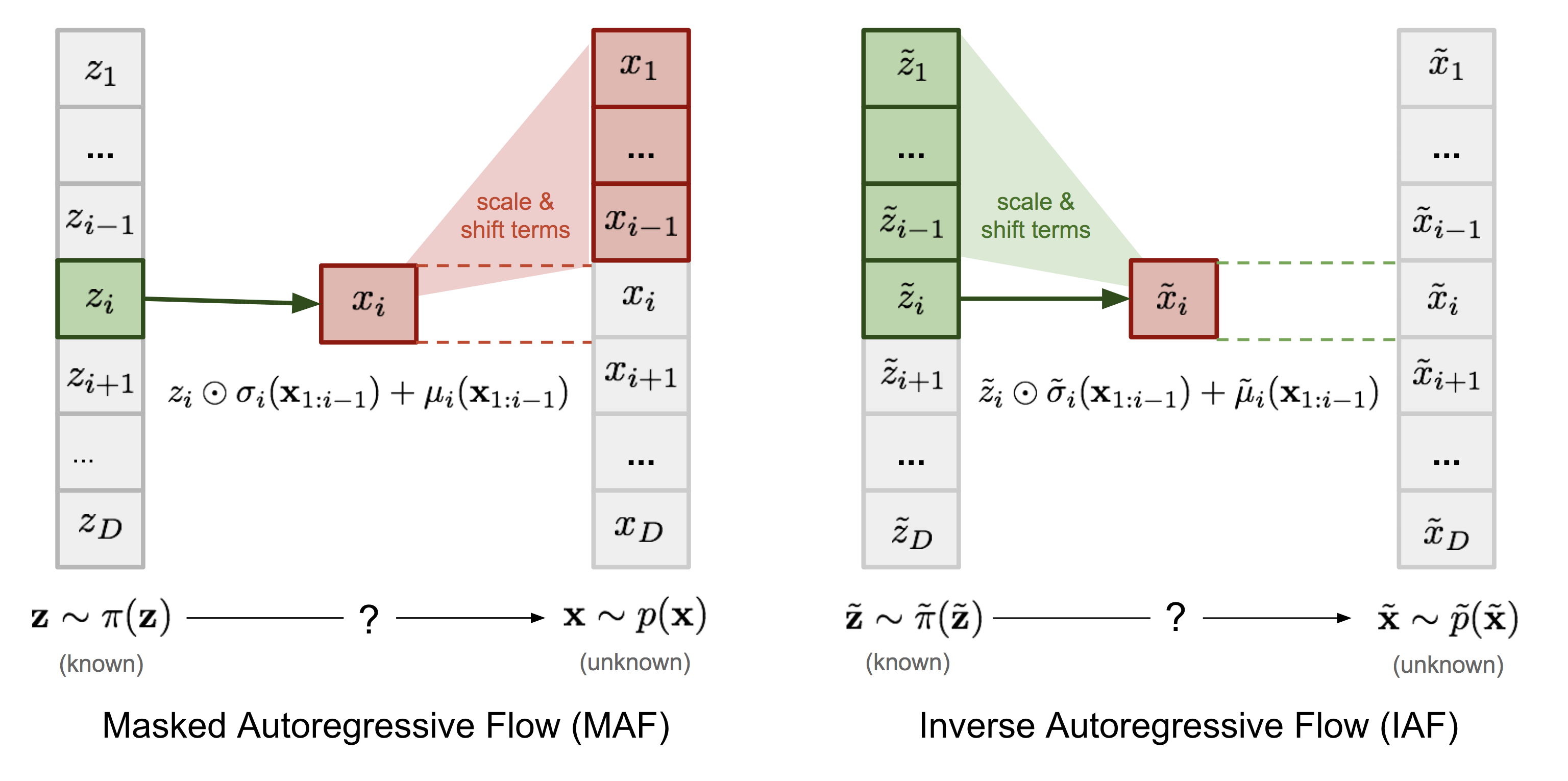
MAF vs IAF comparison
MAF (Masked Autoregressive Flow)
Autoregressive flow where density evaluation is parallel sampling is sequential.
\[ z_i=\frac{x_i-\mu_i(x_{<i})}{\sigma_i(x_{<i})} \]
IAF (Inverse Autoregressive Flow) — fast sampling
Same masked structure but reversed so sampling is parallel (given \(z\)), density is sequential.
\[ x_i=\mu_i(z_{<i})+\sigma_i(z_{<i})\cdot z_i \]
Diffusion Models
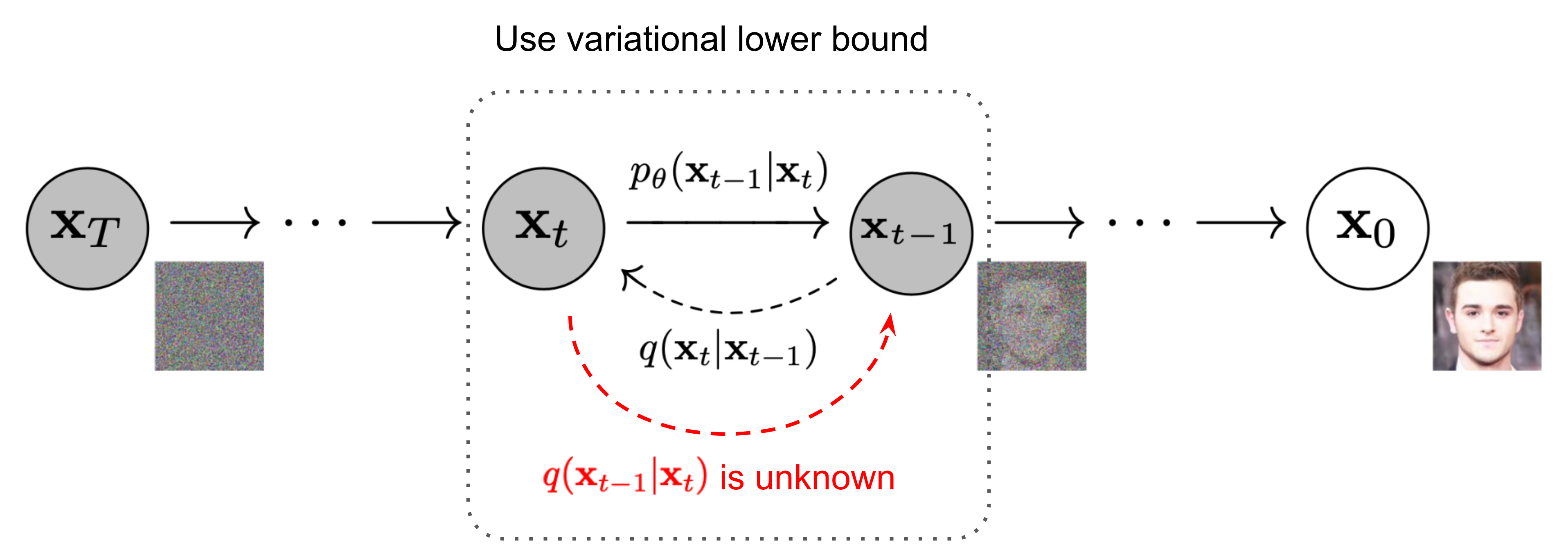
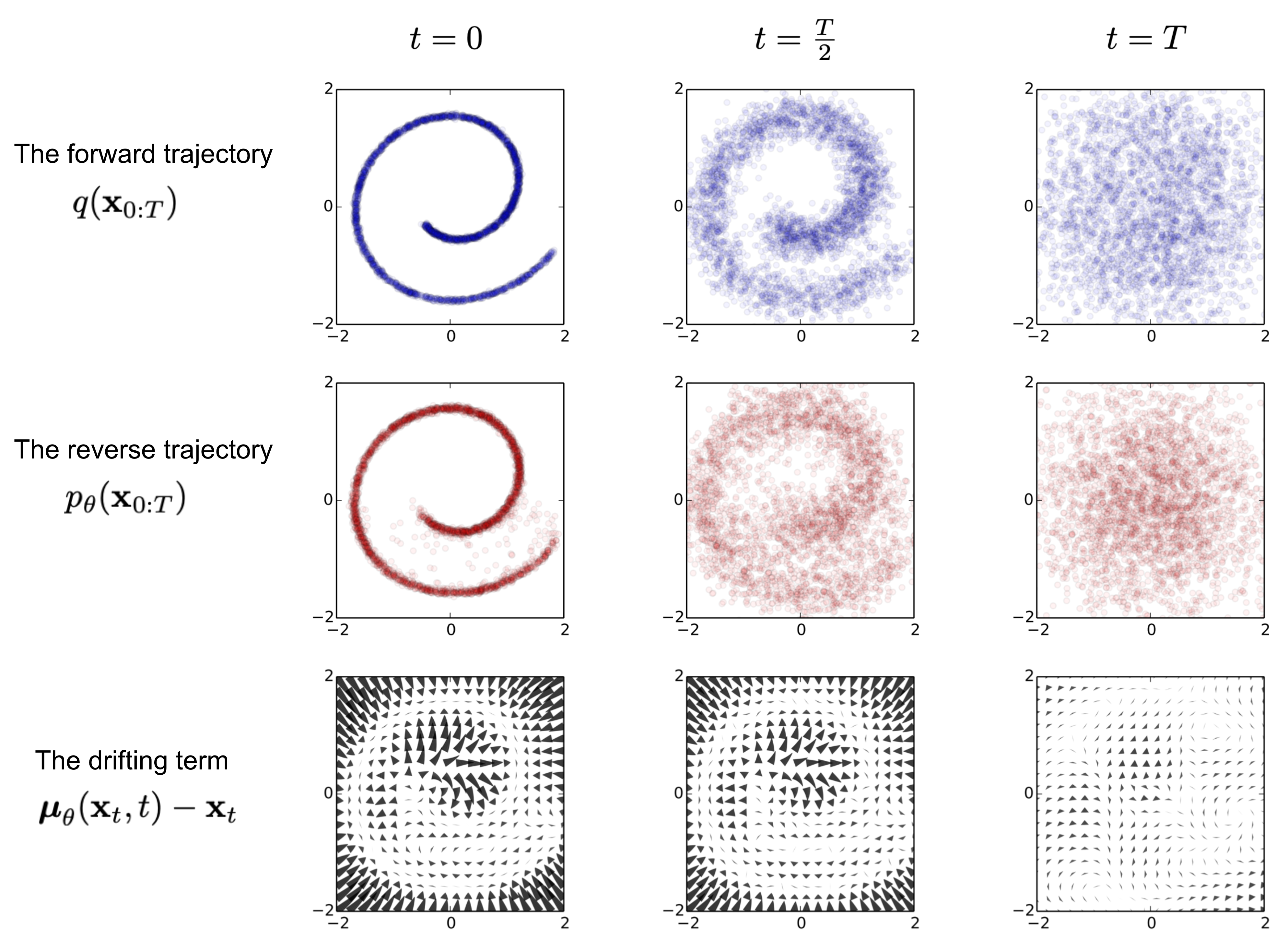

Characteristics of Diffusion Models
Pros:
- Best quality & coverage: diffusion / flow-matching models for images; rapidly improving for video.
Cons:
- High computational cost for training and sampling.
Generative models overview
Generative models overview
| Model | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| VAE | - Explicit likelihood - Fast sampling - Good global structure |
- Blurry outputs - Prior bias (Gaussian) - Limited expressiveness |
| GAN | - Sharp, high-quality images - Fast sampling |
- Training instability - Mode collapse - No likelihood |
| Flow | - Exact likelihood - Invertible - Flexible distributions |
- Computationally expensive - Architecture constraints - Difficult to scale |
| Diffusion | - SOTA quality - Excellent mode coverage - Stable training |
- Slow sampling (many steps) - Computationally intensive - Careful tuning required |
JAX Ecosystem
What is JAX?
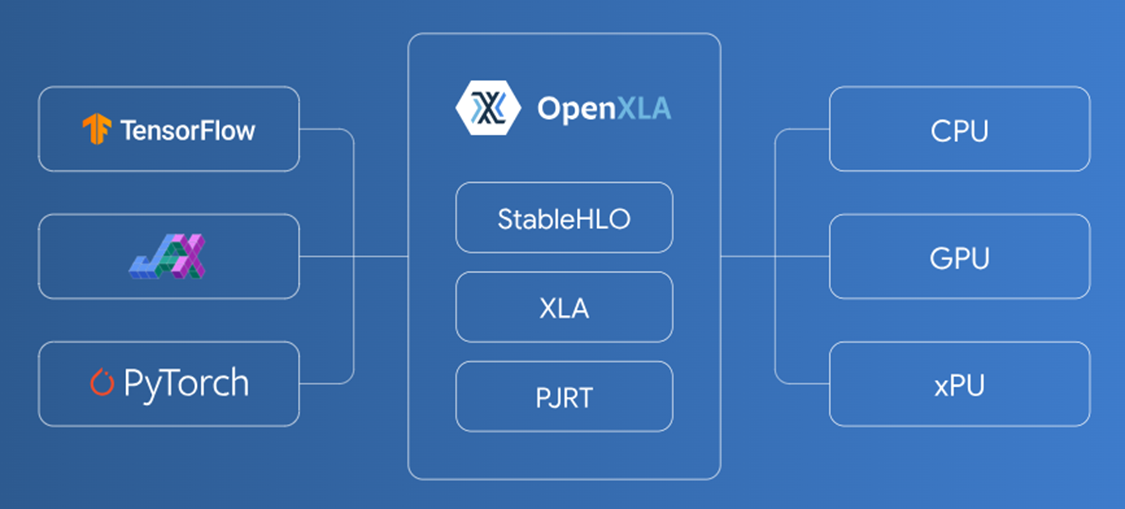
<h2 style="margin:0;">JAX and OpenXLA</h2>JAX transforms
JIT (Just in time compilation)
grad (automatic differentiation)
Multi-device parallelism (shard_map)
import numpy as np
import jax
import jax.numpy as jnp
mesh = jax.sharding.Mesh(np.array(jax.devices()), ('data',))
def double(x):
return x * 2
double_sharded = jax.shard_map(double, mesh=mesh,
in_specs=jax.sharding.PartitionSpec('data', None),
out_specs=jax.sharding.PartitionSpec('data', None))
# shard over axis 0
x = jnp.arange(8).reshape(len(jax.devices()), -1)
y = double_sharded(x)tiny gradient demo
Computing gradients with PyTorch
Computing gradients with JAX
Implications of functional programming
No impure functions
Explicit PRNG keys
Numpy RNG
No inplace mutations
JAX RNG
In general
- All modified variables must be passed explicitly as function arguments and return values.
- All arrays are immutable; use
.at[].set()or similar to create modified copies.
Neural nets in JAX (Flax)
Defining a CNN model in PyTorch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class CNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.c1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 32, 3); self.c2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3)
self.fc = nn.Linear(64*6*6, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.c1(x)); x = F.relu(self.c2(x))
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1); return self.fc(x)
model = CNN()Defining a CNN model in Flax
import jax, jax.numpy as jnp
import flax.linen as nn
class CNN(nn.Module):
@nn.compact
def __call__(self, x):
x = nn.relu(nn.Conv(32, (3,3))(x))
x = nn.relu(nn.Conv(64, (3,3))(x))
x = x.reshape((x.shape[0], -1))
return nn.Dense(10)(x)
model = CNN()
params = model.init(jax.random.PRNGKey(0), jnp.ones((1, 3, 8, 8)))Training step example
One training step in PyTorch
One training step in JAX + Flax + Optax
import jax, jax.numpy as jnp
import optax
from flax.training import train_state
def loss_fn(params, batch):
logits = model.apply(params, batch["x"]) # forward
return optax.softmax_cross_entropy_with_integer_labels(
logits, batch["y"]
).mean()
@jax.jit
def train_step(state, batch):
grads = jax.grad(loss_fn)(state.params, batch)
return state.apply_gradients(grads=grads)
state = train_state.TrainState.create(
apply_fn=model.apply,
params=params,
tx=optax.adam(1e-3),
)
state = train_step(state, batch) # one update stepJAX Ecosystem: an overview
FLAX ![Flax]()
Neural network library for JAX with modules, layers, optimizers, training loops.
Optax ![Optax]()
Gradient processing and optimization library for JAX.
BlackJAX ![BlackJAX]()
MCMC sampling library for JAX with HMC, NUTS, SGLD algorithms.
NumPyro ![NumPyro]()
Probabilistic programming library for JAX with Bayesian modeling and inference.
Diffrax
Differential equation solver library for JAX with ODE, SDE, DDE solvers.
Composability + Trade-offs
Strengths
- NumPy-like API; clean function transforms
- Fast & differentiable via XLA +
jit - Powerful composition:
jit(vmap(grad(...))),shard_mapfor multi-device - Ecosystem: Flax, Optax, BlackJAX, Distrax, Diffrax
Weaknesses
- Steep learning curve (purity, PRNG keys, transformations)
- Fewer off-the-shelf models vs PyTorch
- Some APIs evolving (e.g., sharding tools) → more boilerplate at first

Hands-On: Cosmology Applications
GZ10 Dataset
Galaxy Zoo 10 from MultimodalUniverse:
Dataset statistics:
- ~17,700 galaxy images
- RGB images (256×256 pixels)
- Fields:
gz10_label,redshift,object_id
For this workshop: Downsize to 32×32 or 64×64 for
Explore the dataset
Notebook link : Generative_AI_JAX_GZ10_VAE.ipynb
Example A: Variational Autoencoder for galaxies
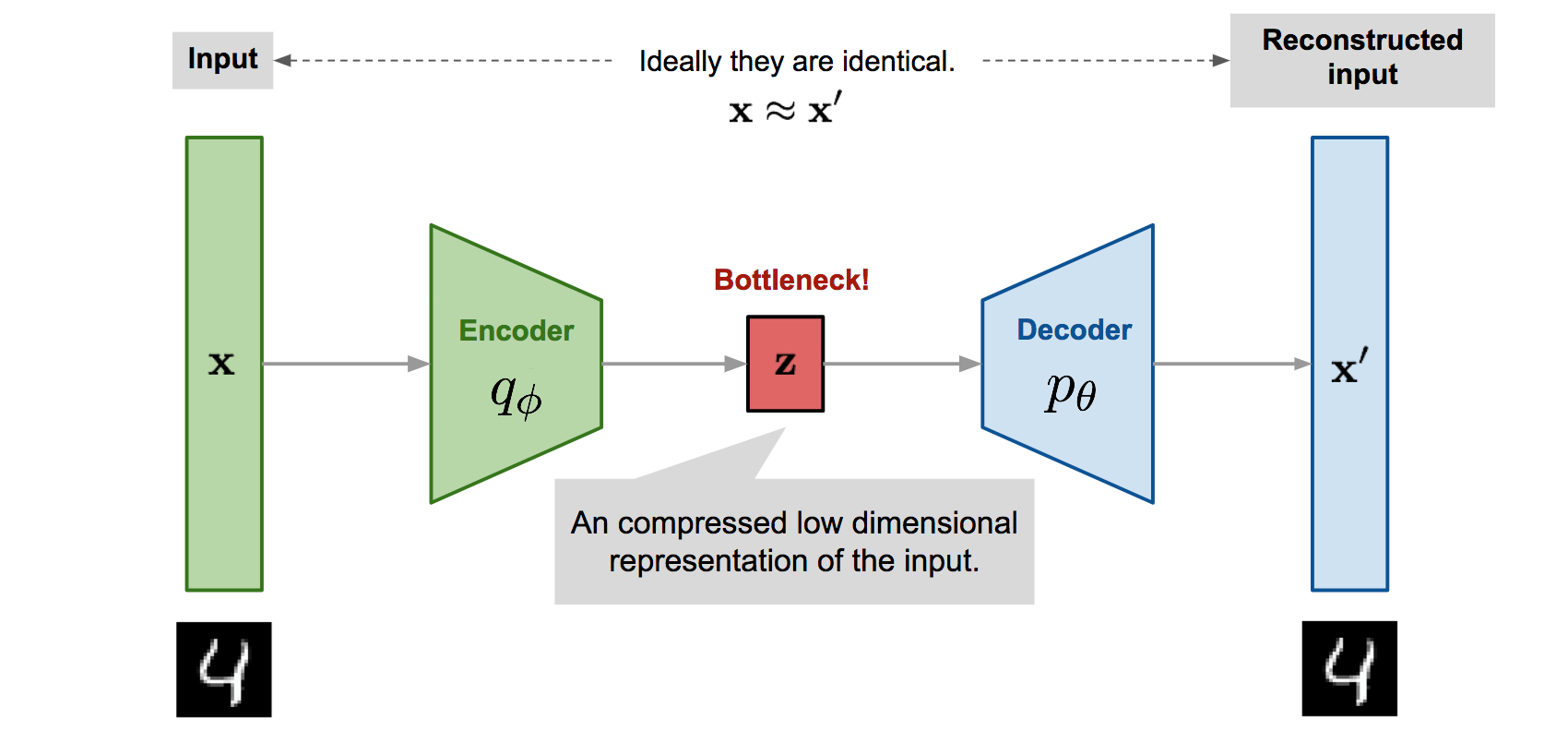
Variational Autoencoder
Train a VAE on GZ10 galaxies and analyze latent space
Notebook link : Generative_AI_JAX_GZ10_VAE.ipynb
Example B : Using a classifier from the latent space

VAE latent space to redshift
Classify galaxy morphology from VAE latent space
Notebook link : Generative_AI_JAX_GZ10_VAE_Classifier.ipynb
AISSAI School 2025


